# Table of Contents
# 스프링 프레임워크의 HTTP 통신
스프링 프레임워크는 HTTP 통신을 위해 다양한 기능을 제공한다.
# RestTemplate
RestTempate은 Spring 3부터 지원하며 멀티 스레드, 동기/블로킹 방식으로 HTTP 요청을 보내는 HTTP Client다.
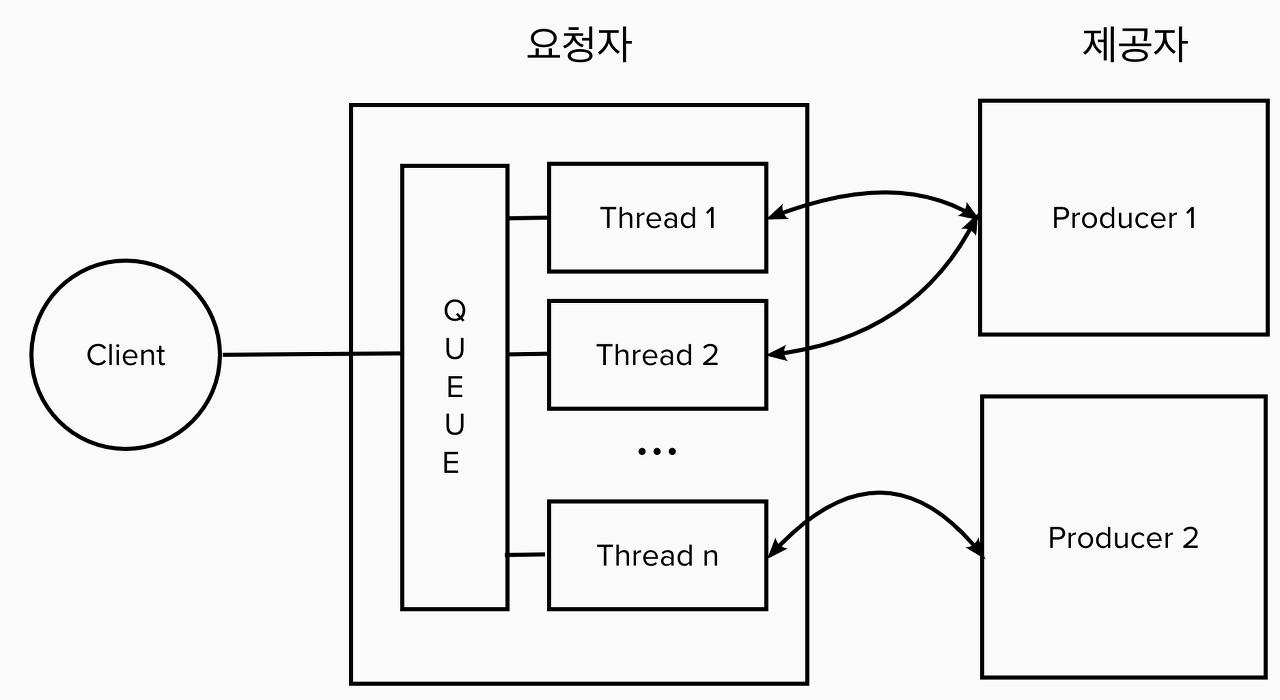
RestTempate은 HTTP 통신을 위한 다양한 메소드를 제공한다.
# getForObject()
서버는 다음과 같은 형태의 JSON 데이터를 반환한다고 가정하자.
{
"email": "paul@gmail.com",
"name": "paul",
"age": "3"
}
getForObject()는 HTTP GET 요청에 사용된다.
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "https://server_url/path";
String response = restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class); // {"email": "paul@gmail.com", "name": "paul", "age": "3"}
JSON 응답을 POJO로 매핑할 수도 있다. 이 때 POJO 클래스는 기본 생성자와 Setter를 반드시 포함해야한다.
public class User implements Serializable {
private String email;
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "https://server_url/path";
User response = restTemplate.getForObject(url, User.class);
# getForEntity()
getForEntity()도 HTTP GET 요청에 사용된다. 다만 응답을 ResponseEntity로 래핑하여 반환한다.
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "https://server_url/path";
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class)
HttpStatus httpStatus = response.getStatusCode();
User user = response.getBody();
HttpHeaders headers = response.getHeaders();
headers.getContentType();
# postForObject()
postForObject()는 HTTP POST 요청에 사용된다.
User user = new User("ronaldo@gmail.com", "ronaldo", 35);
HttpRequest<User> request = new HttpEntity<>(user);
User user = restTemplate.postForObject(url, request, User.class);
# postForEntity()
postForEntity()도 HTTP POST 요청에 사용된다. 다만 응답을 ResponseEntity로 래핑하여 반환한다.
User user = new User("ronaldo@gmail.com", "ronaldo", 35);
HttpRequest<User> request = new HttpEntity<>(user);
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, request, User.class);
postForEntity()는 Form data를 Submit 하는데 사용할 수도 있다.
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
MultiValueMap<String, String> map= new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
map.add("email", "ronaldo@gmail.com");
map.add("name", "ronaldo");
map.add("age", "35");
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, String>> request = new HttpEntity<>(map, headers);
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, request, User.class);
# postForLocation()
postForLocation()도 HTTP POST 요청에 사용된다. 다만 자원이 생성된 위치를 반환한다.
User user = new User("ronaldo@gmail.com", "ronaldo", 35);
HttpRequest<User> request = new HttpEntity<>(user);
URI location = restTemplate.postForLocation(url, request);
# delete()
delete()는 HTTP DELETE 요청에 사용된다.
String url = "http://server/user/1"
restTemplate.delete(url);
# exchange()
exchange()는 RequestEntity을 사용하여 HTTP 요청을 보내고 ResponseEntity를 통해 HTTP 응답을 받는다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseDTO> test(@RequestBody RequestDTO requestDTO) {
ResponseDTO response = new ResponseDTO(requestDTO.getName(), requestDTO.getAge());
HttpHeaders headers= new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Content-type", "application/json");
return new ResponseEntity(response, headers, HttpStatus.ACCEPTED);
}
}
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class TestControllerTest {
@Autowired
TestRestTemplate template;
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Test
public void test() {
RequestDTO body = new RequestDTO("Paul", 35);
HttpHeaders headers= new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Accept", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
headers.add("Content-type", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
URI url = URI.create("http://localhost:" + port + "/test/test1");
RequestEntity<RequestDTO> request = new RequestEntity(body, headers, HttpMethod.POST, url);
ResponseEntity<ResponseDTO> response = template.exchange(request, ResponseDTO.class);
assertThat(response.getBody().getName()).isEqualTo("Paul");
assertThat(response.getBody().getAge()).isEqualTo(34);
}
}
# RestTemplateBuilder
RestTemplateBuilder을 사용하면 빌더 패턴으로 RestTemplate을 생성할 수 있다. 보통 설정도 함께 적용하여 컨테이너에 빈으로 등록하여 사용한다.
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplateBuilder()
.messageConverters(getHttpMessageConverters())
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
.errorHandler(new HttpResponseErrorHandler())
.requestFactory(() -> getClientHttpRequestFactory())
.additionalInterceptors(bearerAuthInterceptor())
.build();
}
}
# TestRestTemplate
테스트 시 RestTemplate 대신 TestRestTemplate을 사용할 수 있다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/person")
public class PersonController {
@GetMapping("/get")
public ResponseEntity<Person> get(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Person p = new Person("Paul", 35);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(p);
}
}
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class Test {
@Autowired
TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void test() {
ResponseEntity<Person> response = template.getForEntity("/person/get", Person.class);
assertThat(response.getStatusCodeValue()).isEqualTo(200);
}
}
# RequestEntity
RestTemplate.exchange()는 RequestEntity을 사용하여 HTTP 요청을 보내고 ResponseEntity를 통해 HTTP 응답을 받는다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseDTO> test(@RequestBody RequestDTO requestDTO) {
ResponseDTO response = new ResponseDTO(requestDTO.getName(), requestDTO.getAge());
HttpHeaders headers= new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Content-type", "application/json");
return new ResponseEntity(response, headers, HttpStatus.ACCEPTED);
}
}
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class TestControllerTest {
@Autowired
TestRestTemplate template;
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Test
public void test() {
RequestDTO body = new RequestDTO("Paul", 35);
HttpHeaders headers= new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Accept", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
headers.add("Content-type", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
URI url = URI.create("http://localhost:" + port + "/test/test1");
RequestEntity<RequestDTO> request = new RequestEntity(body, headers, HttpMethod.POST, url);
ResponseEntity<ResponseDTO> response = template.exchange(request, ResponseDTO.class);
assertThat(response.getBody().getName()).isEqualTo("Paul");
assertThat(response.getBody().getAge()).isEqualTo(34);
}
}
# ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity를 사용하면 HTTP Response를 좀 더 체계적으로 관리할 수 있다.
@PostMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseDTO> test(@RequestBody RequestDTO requestDTO) {
ResponseDTO response = new ResponseDTO();
HttpHeaders headers= new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Content-type", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
return new ResponseEntity(response, headers, HttpStatus.ACCEPTED);
}
